Pesticide Repurposing with KGE
Pesticides are essential for controlling agricultural pests and diseases and increasing crop yields. However, the development of new pesticides requires significant resources and time, leading to a shortage in pesticide supply. Traditional pesticide design methods are heavily reliant on field trials and bioassays for experimental screening, often lacking systematic guidance. To address this limitation, we first propose a novel pesticide repurposing method based on knowledge graph embedding (KGE) and link prediction inspired by drug repurposing. We construct a comprehensive pesticide knowledge graph and use the KGE model to capture the semantic and structural information of the graph. By applying pesticide-disease link prediction techniques, we identify potential new relationships between pesticides and diseases. This approach can effectively generalize to unseen pesticide-disease relationships, providing a scientific foundation and motivation for biochemical experiments in pesticide repurposing. Codes and data are available at: here
Method
Our approach involves several key steps, as illustrated in Figure 1. First, we collect extensive data on pesticides, crops, and diseases from various sources, including encyclopedias, books, product manuals, and government registration websites, to construct a comprehensive pesticide database. Next, we transform this relational data into a graph structure by defining multiple entities and relationships, thereby building the pesticide knowledge graph. Following this, we train a (KGE) model on the pesticide knowledge graph, enabling the embedding matrix to capture both the structural features of the graph and the semantic information of the nodes. Finally, we input a subgraph (composed of multiple triples) into the trained model, extract their embedding vectors from the matrix, and compute the confidence scores. The triple with the highest confidence score is then selected as the predicted result for pesticide repurposing.
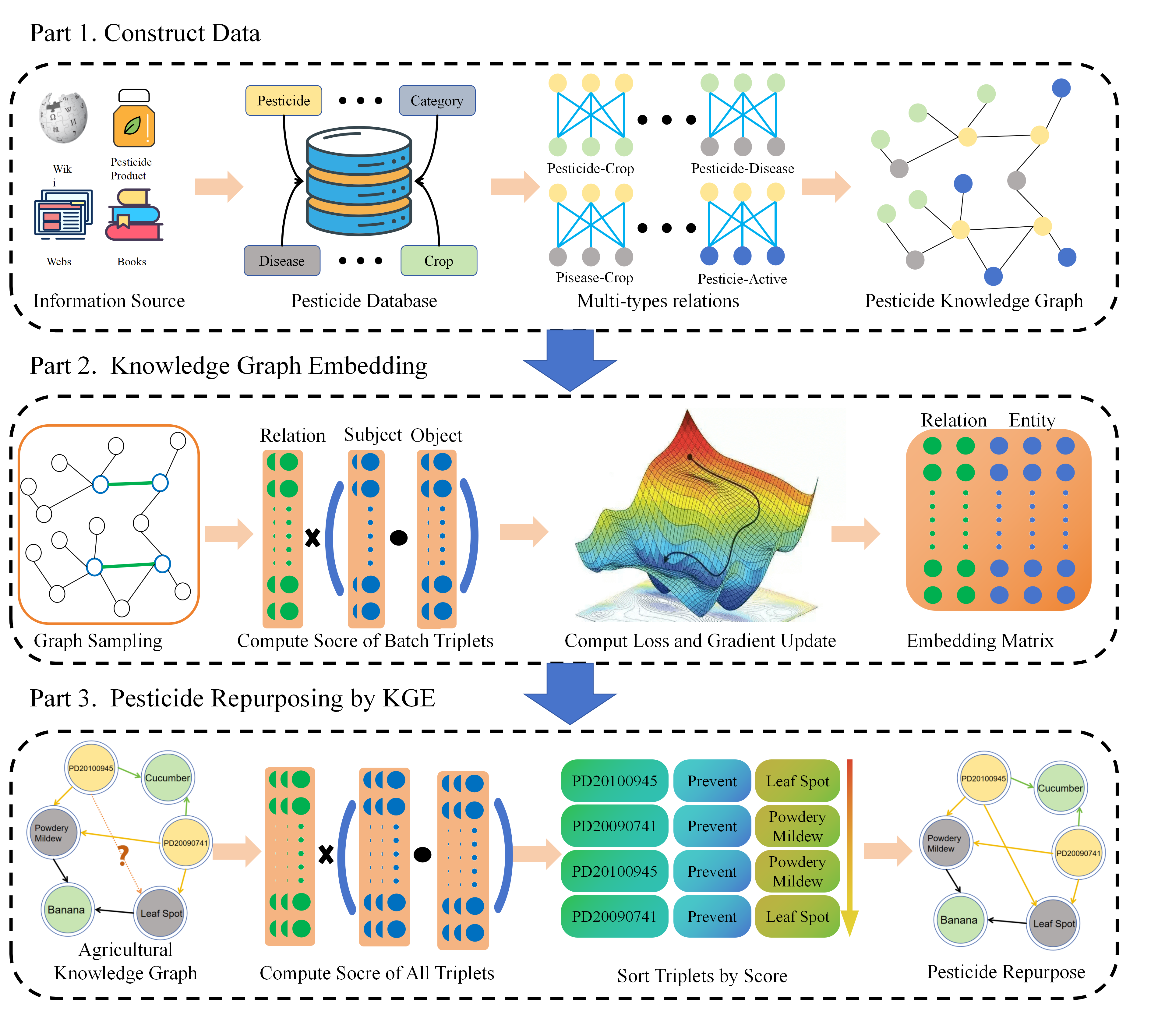
Figure 1. Overview of Pesticide Repurposing with KGE. Part 1: We collect data about pesticides and build a pesticide database and pesticide knowledge graph. Part 2: We train the KGE model through the constructed knowledge graph to obtain the embedding matrix of entities and relations. Part 3: We calculate the confidence of triples through the knowledge graph and embedding matrix to achieve link prediction and pesticide repurposing
Data: Pesticide Knowledge Graph
The pesticide knowledge graph in a visual representation of complex agricultural information, which integrates key entities, such as pesticides, crops, and diseases, and their relationships. Figure 2 presents the conceptual model of the pesticide knowledge graph, emphasizing the central role of pesticides and their connections to other entities, like crops and diseases. This visualization method demonstrates how various types of entities and relationships are organized within the graph structure, helping users to more intuitively understand the complex interactions within the agricultural ecosystem.
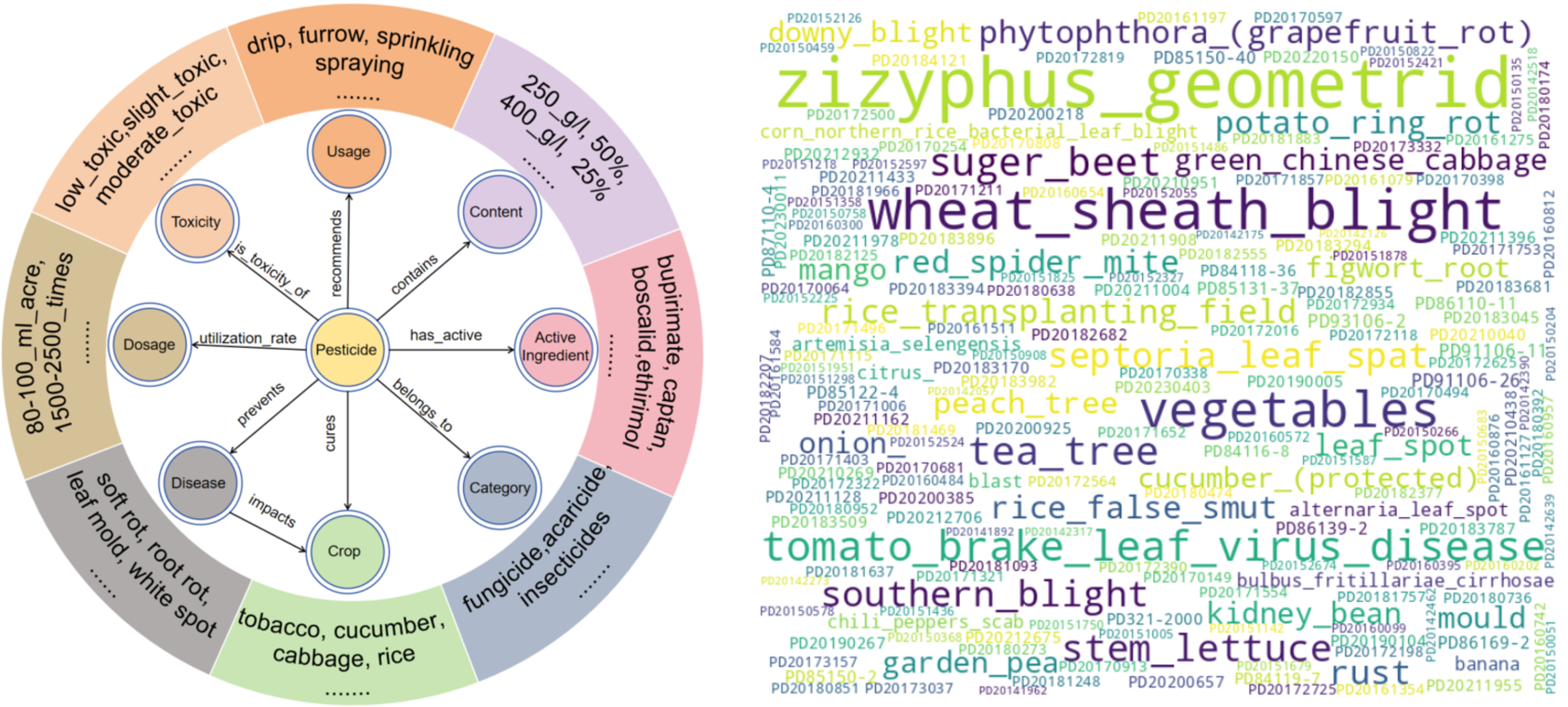
Figure 2. Conceptual Model of Pesticide knowledge graph: The circles represent different types of entities, such as pesticides, crops, etc. The arrows between the circles represent the relationships between entities, such as the relationship between pesticides and crops is cure. The outer rings list specific examples of each entity type, for example, examples of crops include tobacco, cucumber, etc. The word cloud shows the frequency of entity occurrence. It can be seen that crops and diseases appear frequently, while pesticides appear rarely, which is consistent with the scale-free characteristics of the pesticide knowledge graph.
Pesticide Knowledge Graph
We constructed a knowledge graph of agricultural chemicals using the Neo4j graph database, effectively representing the complex relationships between pesticides, crops, and diseases. Figure 3 shows the visualization results of the knowledge graph, intuitively demonstrating how entities are interconnected through different types of relationships.
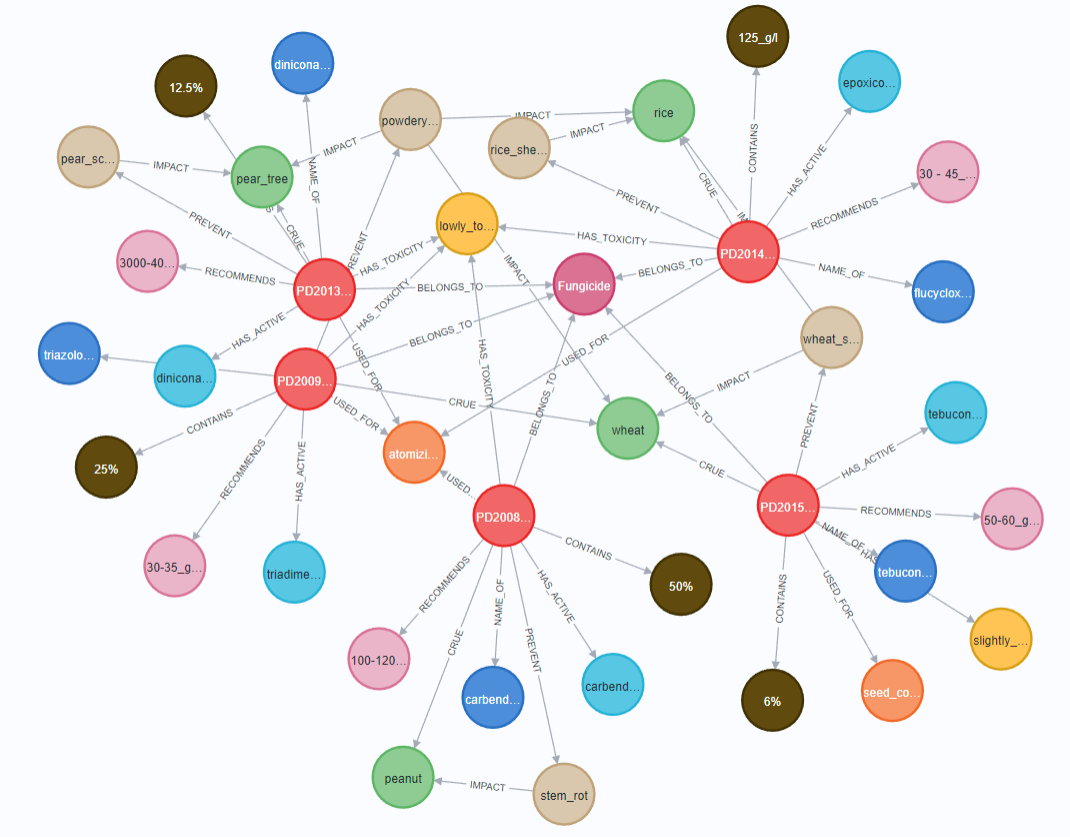
Figure 3. Pesticide knowledge graph in Neo4j: Different colors in the figure represent different entity types. The edge types are marked in text form. The pesticide knowledge graph is highly scale-free. For example, four pesticides can cure wheat, and three diseases can affect wheat.
Pesticide Repurposing with KGE
Based on our proposed method, we can achieve pesticide repurposing through the use of KGE models for link prediction. As shown in Figure 4, upon completion of model training, we utilize the embedding matrix to predict potential new pesticide-disease interactions. Specifically, we construct all possible triples in the form of (Pesticide, Prevents ,Disease ) using the sets of pesticides and diseases, forming the complete set \(T_{all}\). Within this set, some triples are already experimentally validated (positive triples), some are objectively existing but yet to be discovered (neutral triples), and others do not exist (negative triples). We input all these triples into the KGE model, which scores them based on a predefined scoring function.
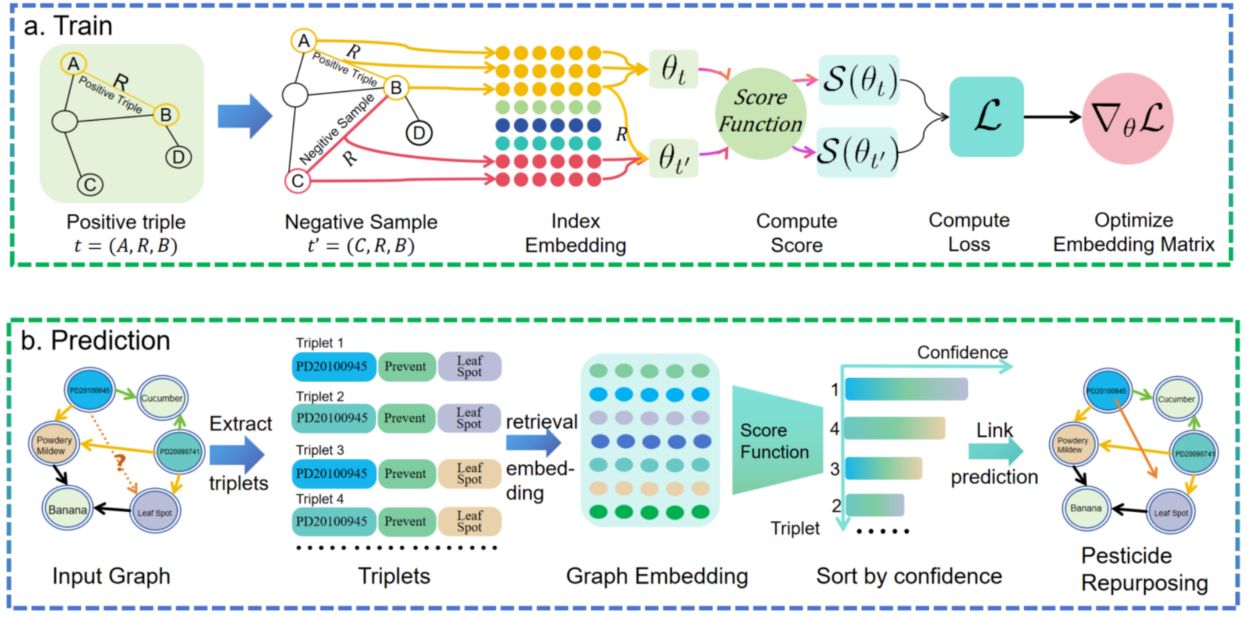
Figure 4. The training and prediction processing of KGE model: (a) Training Process: In the training phase, a batch of positive samples (yellow) is first sampled from the knowledge graph. Negative samples (red) are then generated by randomly perturbing the positive samples. The embedding vectors of the entities and relations in both the positive and negative samples are retrieved from the embedding matrix, and their scores are calculated. The embedding matrix is then optimized using gradient descent based on the scores of the positive and negative samples, as well as the loss function. (b) Prediction Process: During the prediction phase, triplets are extracted from the input graph. The scores and confidence levels of these triplets are calculated using the same method as in training. The triplets are then sorted based on their confidence levels, and the triplet with the highest confidence level is selected as the predicted result.